Occupational Health and safety management standard- ISO 45001:2018
ISO 45001:2018 Occupational Health and Safety Management Standard is the international standard that ensures the safety and well-being of employees in the workplace. This standard helps organizations to proactively identify and manage Occupational safety and health risks and improve overall OHS performance. Implementing ISO 45001:2018 can lead to increased productivity and employee satisfaction, as well as legal compliance and reduction in workplace incidents. In this article you can learn about occupational health and safety in Nepal and its related topics.
What is the ISO 45001:2018 Occupational Health and Safety Management Standard?
ISO 45001:2018 is the latest international standard for Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) management.
It is designed to help organizations improve their Occupational safety and health management system performance and reduce the risk of workplace accidents and injuries.
Occupational Health and Safety in Nepal
Occupational health and safety (OHS) in Nepal is a concern due to a lack of regulations and enforcement, as well as poor working conditions in many industries. The government of Nepal has put in place laws and regulations to protect the health and safety of workers, but enforcement is often weak.
The most common hazards in Nepal include exposure to hazardous chemicals, poor ventilation, and lack of personal protective equipment. The construction and manufacturing sectors, as well as the agriculture and mining industries, are particularly vulnerable to these hazards. Additionally, the country is also prone to natural disasters such as earthquakes and floods, which can have a significant impact on occupational safety and health management system.
However, there are some efforts being made to improve Occupational safety and health in Nepal. The government has established the Department of Labour and Employment Promotion (DoLEP) which is responsible for enforcing labour laws and promoting safe and healthy working conditions. Additionally, international organizations, such as the International Labour Organization (ILO), have been working with the Nepalese government and private sector to improve Occupational health and safety through training, awareness-raising and capacity building.
However, the country still has a long way to go to ensure safe and healthy working conditions for all workers. The government and private sectors need to work together to improve occupational health and safety in Nepal. Also, the workers themselves must be educated and trained to be aware of the risks and how to protect themselves.
Occupational health and safety laws in Nepal
Occupational health and safety (OHS) laws in Nepal include:
The Labour Act, 2074 (2017) which provides for the rights and welfare of workers, and establishes the Department of Labour and Employment Promotion (DoLEP) to enforce labour laws and promote safe and healthy working conditions.
The Factories and Factory Workers Act, 2049 (1992) which sets regulations for the operation of factories and the protection of factory workers.
The Mines and Minerals Act, 2053 (1997) which regulates the mining industry and the safety of mine workers.
The Construction Workers' Welfare Act, 2061 (2004) which provides for the welfare of construction workers and regulates the construction industry.
Occupational health and safety act Nepal
The Occupational safety and health (OHS) Act Nepal is not exist. However, Nepal has several laws and regulations that pertain to OHS, as mentioned above.
Occupational health and safety plan and policy
The Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) Plan and Policy in Nepal may include:
A comprehensive hazard identification and risk assessment process to identify and evaluate hazards in the workplace.
Procedures for incident reporting and investigation to ensure that incidents are properly investigated and that lessons are learned to prevent future incidents.
Training and education programs to educate employees on Occupational health and safety topics, including how to identify hazards, how to prevent injuries and illnesses, and how to respond in case of an emergency.
Emergency response plans to ensure that employees know how to respond in case of an emergency.
Regular inspections and audits to ensure that employees are following occupational health and safety policies and procedures and that the company is in compliance with all relevant laws and regulations.
Procedures for managing workers' compensation claims, including coordinating medical treatment and working with insurance providers to ensure that employees receive the benefits they are entitled to.
A process for evaluating the effectiveness of the Occupational safety and health plan and making improvements as needed.
It's important to note that, while Nepal has laws and regulations in place to protect the health and safety of workers, enforcement can be weak, and the country still has a long way to go to ensure safe and healthy working conditions for all workers.
Why is ISO 45001:2018 Important?
ISO 45001:2018 is important because it provides a framework for organizations to manage Occupational health and safety risks and improve their overall Occupational safety and health performance.
The standard helps organizations to identify and control hazards, reduce the likelihood of accidents, and improve the overall well-being of employees. Additionally, it helps organizations to meet legal and regulatory requirements, and to improve their reputation and competitiveness in the marketplace.
Occupational Health and Safety specialist
An occupational health and safety (OHS) specialist at ISO Certification in Nepal Pvt. Ltd. would be responsible for ensuring that the company's policies, procedures, and practices meet or exceed local, national, and international OHS standards. Some specific responsibilities of an Occupational safety and health specialist in this role may include:
Developing and implementing OHS policies and procedures: This includes identifying hazards, assessing risks, and developing strategies to mitigate those risks.
Conducting regular inspections and audits: The Occupational health and safety specialist would conduct regular inspections and audits to ensure that all employees are following OHS policies and procedures and that the company is in compliance with all relevant laws and regulations.
Providing OHS training and education: The Occupational safety and health specialist would be responsible for providing training and education to employees on OHS topics, including how to identify hazards, how to prevent injuries and illnesses, and how to respond in case of an emergency.
Investigating incidents and near-misses: When incidents or near-misses occur, the occupational health and safety specialist would investigate the cause and make recommendations to prevent similar incidents in the future.
Managing workers compensation claims: The occupational safety and health specialist would manage the process of workers compensation claims, including coordinating medical treatment and working with insurance providers to ensure that employees receive the benefits they are entitled to.
Collaborating with other departments: The occupational health and safety specialist would work closely with other departments within the company, such as human resources and operations, to ensure that OHS is integrated into all aspects of the company's operations.
Keeping up to date with relevant laws, regulations and standards: The occupational safety and health specialist would be responsible for staying up to date with all relevant laws, regulations and standards related to OHS.
What are the Key Elements of ISO 45001:2018?
ISO 45001:2018 is based on the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, which is a systematic approach to management. The key elements of the standard include:
- Leadership and commitment: Organizations are required to demonstrate commitment to OHS at all levels of the organization and to provide leadership in occupational health and safety matters.
- Policy and objectives: Organizations are required to establish a policy and objectives for Occupational health and safety, and to communicate them to all employees.

3. Planning: Organizations are required to identify hazards and assess risks, and to develop and implement plans to control those risks.
4. Implementation and operation: Organizations are required to implement and maintain their occupational health and safety management system, and to provide resources and training to support it.
Evaluation and review: Organizations are required to evaluate and review their occupational safety and health performance, and to take corrective and preventive action as needed.
How Can Organizations Achieve Compliance with ISO 45001:2018?
Organizations can achieve compliance with ISO 45001:2018 by implementing an occupational health and safety management system that meets the requirements of the standard. This will typically involve a process of assessment, planning, implementation, and review. Organizations may also choose to seek third-party certification to demonstrate their compliance with the standard.
Benefits of ISO 45001:2018
- Improved stakeholder relationships: ISO 45001:2018 offers a wide range of benefits for organizations. One of the key benefits is improved stakeholder relationships. By implementing an occupational health and safety management system that meets the requirements of the standard, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to occupational safety and health to their stakeholders, including employees, customers, and suppliers.
- Improved risk management: Another key benefit of ISO 45001:2018 is improved risk management. The standard provides a framework for organizations to identify and control hazards, reduce the likelihood of accidents, and improve the overall well-being of employees. This can lead to reduced workplace accidents and injuries, and improved employee well-being.
- Legal compliance: ISO 45001:2018 also helps organizations to meet legal and regulatory requirements, and to comply with health and safety law. This can reduce the risk of legal liability and fines, and improve the organization's reputation.
- Compliance with health and safety law: By implementing an occupational health and safety management system that meets the requirements of the standard, organizations can ensure compliance with occupational safety and health laws and regulations.
- Improved employee well-being and engagement: By promoting a culture of health and safety and providing resources and training to support employees, organizations can improve the well-being and engagement of their employees.
- Reduced workplace accidents and injuries: By implementing effective controls and procedures, organizations can reduce the number of workplace accidents and injuries, which can lead to cost savings and improved productivity.
- Improved reputation and competitiveness in the marketplace: By demonstrating commitment to occupational health and safety, organizations can improve their reputation and competitiveness in the marketplace, which can lead to increased business opportunities.
- Improved efficiency and productivity: By implementing an occupational health and safety management system that is based on the PDCA cycle, organizations can continuously improve their occupational safety and health performance and efficiency, which can lead to increased productivity.
- Improved decision making through data analysis and evaluation: By collecting and analyzing data on their occupational health and safety performance, organizations can make more informed decisions and take corrective and preventive action as needed.
key performance indicators for occupational health and safety
Some key performance indicators (KPIs) for occupational health and safety (OHS) include:
Incident rate: The number of incidents per number of workers or hours worked.
Injury rate: The number of injuries per number of workers or hours worked.
Lost time injury rate: The number of injuries that result in missed work days per number of workers or hours worked.
Near miss rate: The number of near misses per number of workers or hours worked.
Compliance rate: The percentage of compliance with relevant occupational health and safety laws, regulations, and standards.
Training completion rate: The percentage of workers who have completed required occupational health and safety training.
Audit or inspection pass rate: The percentage of audits or inspections that pass with no major violations.
Employee engagement: The level of employee engagement in occupational health and safety programs and initiatives.
Return to work rate: The percentage of employees who return to work after an injury or illness.
Cost of incidents: The cost of incidents in terms of workers' compensation, medical expenses, and lost productivity.
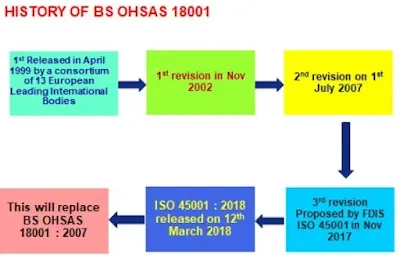
What does ISO 45001:2018 replace?
ISO 45001:2018 replaces the previous standard for Occupational safety and health management, OHSAS 18001:2007. OHSAS 18001:2007 was a widely used standard for occupational health and safety management, but it was not developed or published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
ISO 45001:2018 is the first international standard for Occupational safety and health management system that was developed by the ISO and it's the first standard that follows the high-level structure and common text of the ISO management system standards.
Organizations that were previously certified to OHSAS 18001:2007 will need to transition to ISO 45001:2018 by a certain date, as OHSAS 18001:2007 will be withdrawn and will no longer be valid. The transition period for OHSAS 18001:2007 certification holders to upgrade to ISO 45001:2018 will be 3 years from the date of publication of ISO 45001:2018.
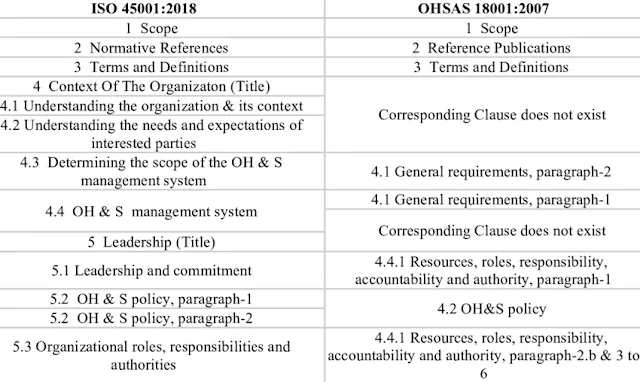
what is difference between ISO 45001 and OHSAS 18001?
ISO 45001 and OHSAS 18001 are both international standards for Occupational Health and Safety (OH&S) management systems. Both of these standards aim to provide a framework for organizations to identify and manage potential hazards in the workplace, minimize risks and improve overall performance. However, there are some key differences between the two standards that organizations should be aware of.
The main difference between ISO 45001 and OHSAS 18001 is that ISO 45001 is a globally recognized standard, while OHSAS 18001 is a recognized standard in the UK and some other countries. ISO 45001 was developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and is based on the High-Level Structure (HLS), which is a common framework used for the development of management system standards. On the other hand, OHSAS 18001 was developed by a group of international experts and is not based on the HLS.
Another significant difference between the two standards is the level of emphasis on leadership and worker participation. ISO 45001 places a greater emphasis on leadership and worker participation in the OH&S management process, whereas OHSAS 18001 focuses more on the management system itself. Additionally, ISO 45001 includes specific requirements for the management of risks and opportunities, while OHSAS 18001 does not.
ISO 45001 also requires organizations to have a more robust risk management process in place, which includes identifying hazards, assessing risks, implementing controls, and monitoring performance. The standard also requires organizations to conduct internal audits and management reviews to ensure the OH&S management system is effective.
Auditors view on ISO 45001:2018
From an auditor's perspective, ISO 45001:2018 is a well-structured standard that provides a clear and comprehensive framework for Occupational safety and health management system. The standard is based on the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, which is a systematic approach to management that is familiar to auditors and it's also easy to follow.
The standard requires organizations to establish a clear occupational health and safety policy and objectives, which are communicated throughout the organization, and it also requires organizations to have a clear leadership and commitment in OHS matters. This is important for auditors, as it ensures that occupational health and safety is given the priority it deserves within the organization.
ISO 45001:2018 also includes a number of new requirements for risk management, which is a key aspect of OHS management. The standard requires organizations to identify and control hazards, assess risks, and take corrective and preventive action as needed. This is an important aspect of occupational safety and health management system, and it is well-aligned with the risk-based thinking approach that is used in other ISO management system standards.
Another important aspect of the standard is the requirement for organizations to collect and analyze data on their occupational health and safety performance, and to take corrective and preventive action as needed. This is important for auditors, as it helps to ensure that organizations are continuously improving their occupational safety and health performance.
ISO 45001:2018 OHSMS Auditing
The auditing process for ISO 45001:2018 includes a series of steps that are designed to ensure that the organization's OHSMS is in compliance with the standard. These steps include:
Planning: The auditor will plan the audit by reviewing the organization's occupational safety and health management system documentation, identifying areas of focus, and scheduling the audit.
Opening meeting: The auditor will conduct an opening meeting with the organization's management team to introduce the audit team, explain the audit process, and establish the scope and objectives of the audit.
Document review: The auditor will review the organization's OHSMS documentation, including the occupational health and safety policy, procedures, and records, to ensure that they meet the requirements of the standard.
On-site audit: The auditor will conduct an on-site audit of the organization's occupational safety and health management system, including observation of processes and activities, interviews with employees, and examination of records and documentation.
Closing meeting: The auditor will conduct a closing meeting with the organization's management team to discuss any non-conformities identified during the audit and to provide feedback on the organization's OHSMS.
Report: The auditor will prepare a report that summarizes the findings of the audit, including any non-conformities identified and any recommendations for improvement.
Follow-up: The auditor will conduct a follow-up audit to verify that the organization has taken corrective and preventive action to address any non-conformities identified during the initial audit.
The auditing process for ISO 45001:2018 is designed to be objective, impartial, and independent. Auditors are trained to understand the requirements of the standard and to evaluate the organization's occupational safety and health against those requirements.
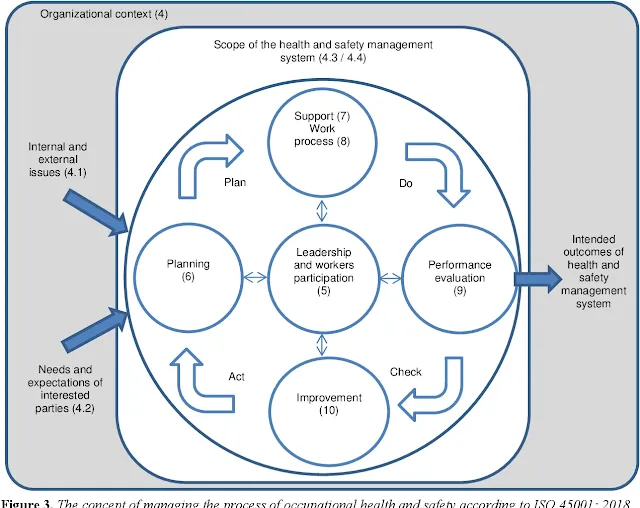
What are the clauses of ISO 45001:2018?
ISO 45001:2018 is divided into 10 clauses, each of which covers a specific aspect of Occupational Health and Safety management System.
These clauses are:
Clause 1: Scope
ISO 45001:2018 applies to any organization, regardless of size, type, or industry. It provides a comprehensive approach to managing occupational health and safety and can be integrated with other management systems, such as ISO 9001 for Quality Management and ISO 14001 for Environmental Management.
The standard covers all aspects of occupational safety and health, including risk management, incident investigation, emergency preparedness, and communication. It also includes requirements for continuous improvement and the involvement of workers in the management of occupational health and safety.
Clause 2: Normative references
ISO 45001:2018 makes reference to other standards, including ISO 9001:2015 for Quality Management Systems and ISO 14001:2015 for Environmental Management Systems. These references ensure that the standard is consistent with other management systems and that organizations can easily integrate their health and safety management system with their quality and environmental management systems.
Additionally, ISO 45001:2018 references the International Labor Organization's (ILO) Occupational Health and Safety Convention, which provides guidance on worker participation, rights, and responsibilities. This reference ensures that the standard is in line with international labor standards and promotes the protection of worker rights.
Clause 3: Terms and definitions
ISO 45001:2018, the international standard for Occupational Health and Safety (OH&S) management systems, includes a number of terms and definitions that are used throughout the standard. These include:
OH&S management system: A framework for an organization to manage its occupational safety and health risks and opportunities, with the aim of improving its overall performance in this area.
Occupational health and safety: The overall well-being of employees and other persons who may be affected by the organization's activities, including physical and mental health, safety and welfare.
Risk: The likelihood of occurrence of harm and the potential severity of that harm.
Opportunity: A potential positive outcome that can be realized by taking advantage of a situation or condition.
Hazard: A source or situation with the potential to cause harm.
Incident: An event that resulted in, or had the potential to result in, harm or injury.
OH&S performance: The results achieved by an organization in relation to its occupational health and safety management system and its occupational safety and health objectives.
OH&S objectives: Specific, measurable targets that an organization sets to improve its OH&S performance over time.
OH&S policy: A statement of an organization's overall intentions and direction in relation to its OH&S management system.
OH&S management program: The set of specific activities and procedures that an organization undertakes to achieve its OH&S objectives and implement its OH&S policy.
Competence: The knowledge, skills and abilities required to perform a specific task or role.
Communication: The exchange of information and understanding between two or more parties.
Consultation: The process of seeking and considering the views and opinions of stakeholders on matters related to OH&S.
Participation: The active involvement of employees and other persons in the design, implementation and review of an organization's occupational health and safety management system.
ISO 45001 Clause 4: Context of the organization
ISO 45001 clause 4 is divided into four sub clause- 4.1,4.2,4.3, and 4.4
4.1 Understanding the organization and its context
This clause refers to the process of understanding the organization and its environment, including external and internal factors that may impact the organization's occupational health and safety management system.
4.1.1 Determine external and internal issues
This subclause refers to the process of identifying and assessing external and internal factors that may impact the organization's occupational health and safety management system. These factors may include things like changes in legislation, new technologies, or changes in the organization's operations.

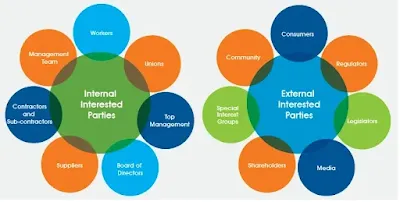
4.2 Understanding the needs and expectations of workers and other interested parties
Understanding the needs and expectations of workers and other interested parties - This clause refers to the process of understanding the needs and expectations of workers and other parties who may be affected by the organization's occupational health and safety management system.
4.2.1 Identify the other interested parties
This subclause refers to the process of identifying other parties who may be affected by the organization's occupational health and safety management system. These parties may include workers, customers, suppliers, or members of the community.
4.2.2 Clarify the needs and expectations
This subclause refers to the process of clarifying the needs and expectations of the identified parties. This may involve conducting surveys, interviews, or focus groups to gather information about the parties' needs and expectations.
4.2.3 Determine legal requirements
This subclause refers to the process of determining the legal requirements that the organization must comply with in order to operate its occupational health and safety management system. This may include identifying relevant laws, regulations, and standards that the organization must comply with.
4.3 Determining the scope of the OH&S management system
Clause 4.3 of ISO 45001 outlines the process for determining the scope of the Occupational Health and Safety (OH&S) management system. This clause states that the scope of the OH&S management system (OH&SMS) should be defined, taking into account external and internal issues, the requirements of interested parties, and the work-related activities of the organization.
4.3.1 Take into account the external and internal issues
Subclause 4.3.1 states that organizations should take into account external and internal issues when defining the scope of their OH&SMS. This includes considering factors such as laws and regulations, industry standards, and any other external factors that may impact the organization's OH&S performance.
4.3.2 Take into account the requirements of interested parties
Subclause 4.3.2 states that organizations should also take into account the requirements of interested parties when defining the scope of their OH&SMS. This includes considering the needs and expectations of employees, customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders who may be impacted by the organization's OH&S performance.
4.3.3 Take into account the work-related activities
Subclause 4.3.3 states that organizations should consider the work-related activities of the organization when defining the scope of their OH&SMS. This includes identifying the specific processes, products, and services that may impact the organization's OH&S performance.
4.3.4 Include in the OH&SMS the activities that can impact the organization's OH&S performance
Subclause 4.3.4 states that organizations should include in the scope of their OH&SMS any activities that can impact the organization's OH&S performance. This includes identifying potential hazards and risks associated with these activities and developing plans to mitigate them.
4.3.5 Retain the scope of the OH&SMS available as documented information
Subclause 4.3.5 states that organizations should retain the scope of their OH&SMS as documented information. This includes maintaining records of the scope of the OH&SMS and any updates made to it, in order to ensure that the organization's OH&S performance is continuously monitored and improved.
4.4 OH&S management system
This clause outlines the overall management system that an organization must establish and maintain in order to control and improve its occupational health and safety performance.
4.4.1 Identify and manage the OH&S risks and opportunities
This subclause requires organizations to identify and assess the risks and opportunities related to occupational health and safety, and to implement measures to control or exploit them as appropriate.
4.4.2 Establish OH&S objectives and targets
This subclause requires organizations to establish measurable objectives and targets for improving their occupational health and safety performance, and to communicate these to all employees and relevant stakeholders.
4.4.3 Implement and maintain the OH&SMS processes
This subclause requires organizations to establish and implement a set of processes for managing occupational health and safety, and to maintain these processes to ensure they remain effective over time.
4.4.4 Continuously monitor and measure the OH&S performance
This subclause requires organizations to establish and implement a system for monitoring and measuring their occupational health and safety performance, and to use this information to identify areas for improvement.
4.4.5 Continuously improve the OH&SMS through regular reviews and audits.
This subclause requires organizations to conduct regular reviews and audits of their occupational health and safety management system, and to use the results of these reviews to identify and implement improvements.
ISO 45001 Clause 5: Leadership and worker participation
ISO 45001 clause 5 is divided into four sub clause- 5.1,5.2,5.3, and 5.4
5.1 Leadership and commitment
Clause 5 of ISO 45001 focuses on leadership and worker participation in the management of Occupational Health and Safety (OH&S).
It lays out the responsibilities of leadership in ensuring the overall success of the OH&S management system.
5.1.1 Assume overall responsibility and accountability for the OH&S prevention
This subclause states that leadership must take ownership of the OH&S management system and be held accountable for its success.
5.1.2 Ensure that the OH&S policy and objectives are established
Leadership must ensure that a clear and comprehensive OH&S policy and objectives are established and communicated throughout the organization.
5.1.3 Ensure that OH&SMS requirements are integrated into the internal business processes
The OH&S management system must be integrated into the organization's internal processes in order to effectively manage OH&S.
5.1.4 Ensure that the necessary resources for the OH&SMS are available
Leadership must ensure that the organization has the necessary resources to implement and maintain the OH&S management system.
5.1.5 Communicate the importance of an effective and conforming OH&SMS
Leadership must communicate the importance of an effective and conforming OH&S management system to all employees and stakeholders.
5.1.6 Ensure the achievement of intended results of the OH&SMS
This clause requires the organization to take necessary actions to ensure that their OH&SMS (Occupational Health and Safety Management System) is achieving its intended goals and objectives.
5.1.7 Support the staff contribution to the effectiveness of the OH&SMS
This clause encourages the organization to support and involve their employees in the implementation and continuous improvement of their OH&SMS.
5.1.8 Promote continual improvement
This clause requires the organization to continuously improve their OH&SMS by regularly reviewing and updating it based on feedback and performance data.
5.1.9 Support the leadership of managers
This clause encourages the organization to provide their managers with the necessary resources, training, and support to effectively lead and implement the OH&SMS.
5.1.10 Promote a culture that supports the intended results of the OH&SMS
This clause requires the organization to create a culture within the workplace that promotes and supports the goals and objectives of their OH&SMS.
5.1.11 Protect workers from reprisals
This clause requires the organization to protect their employees from any negative consequences or retaliation for raising concerns or reporting incidents related to OH&S.
5.1.12 Establish and implement a process for consultation and participation of workers
This clause requires the organization to establish a process for consulting and involving their employees in the development, implementation, and continuous improvement of their OH&SMS.
5.1.13 Support health and safety committees
This clause requires organizations to support health and safety committees, which are groups of workers and management representatives that work together to identify and address health and safety issues in the workplace.
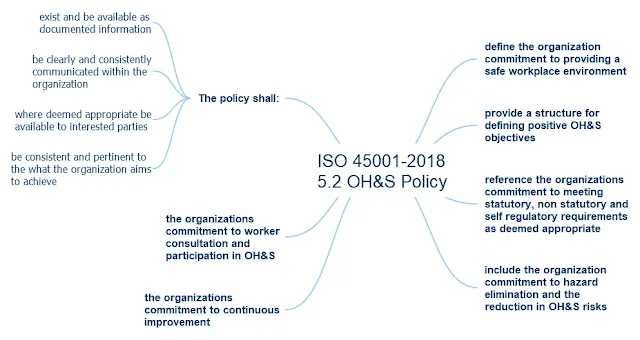
5.2 OH&S policy
This clause covers the organization's Occupational Health and Safety (OH&S) policy.
It outlines the organization's commitment to providing safe and healthy working conditions and provides a framework for defining and reviewing OH&S objectives.
5.2.1 Commit to providing safe and healthy working conditions
This subclause commits the organization to providing safe and healthy working conditions for all workers.
5.2.2 Provide a framework to define and review the OH&S objectives
This subclause provides a framework for defining and reviewing the organization's OH&S objectives.
5.2.3 Meet the applicable legal requirements
This subclause requires the organization to meet all applicable legal requirements related to occupational health and safety.
5.2.4 Commit to eliminate hazards
This subclause commits the organization to eliminating hazards in the workplace.
5.2.5 Commit to OH&SMS continual improvement
This subclause commits the organization to continually improving its Occupational Health and Safety Management System (OH&SMS).
5.2.6 Commit to consultation of workers
This subclause commits the organization to consulting with workers on health and safety issues.
5.2.7 Retain the OH&S policy as documented information
This subclause requires the organization to retain the OH&S policy as documented information.
5.2.8 Communicate the OH&S policy
This subclause requires the organization to communicate its OH&S policy to all workers and interested parties.
5.2.9 Keep the OH&S policy available to interested parties
This subclause requires the organization to make the OH&S policy available to interested parties.
5.2.10 Ensure that the OH&S policy is relevant and appropriate
This subclause requires the organization to ensure that its OH&S policy is relevant and appropriate for the organization and its operations.
5.3 Organizational roles, responsibilities and authorities
Clause 5.3 of ISO 45001 outlines the organizational roles, responsibilities and authorities for the Occupational Health and Safety Management System (OH&SMS).
5.3.1 Ensure that OH&SMS responsibilities and authorities are assigned
Subclause 5.3.1 states that the organization must ensure that OH&SMS responsibilities and authorities are assigned to appropriate individuals or groups within the organization. This means that specific roles and responsibilities for managing and implementing the OH&SMS must be clearly defined and assigned to individuals or teams within the organization.
5.3.2 Maintain OH&SMS responsibilities and authorities as documented
Subclause 5.3.2 requires the organization to maintain documentation of the OH&SMS responsibilities and authorities that have been assigned. This documentation should be kept up-to-date and accessible to all relevant parties.
5.3.3 Assume (by the workers) the responsibility for the elements of the OH&SMS for which they are responsible
Subclause 5.3.3 states that workers must assume responsibility for the elements of the OH&SMS for which they are responsible. This means that individuals within the organization must take ownership of their specific roles and responsibilities within the OH&SMS and actively work to fulfill them.
5.3.4 Ensure that the OH&SMS meets the requirements of ISO 45001
Subclause 5.3.4 requires the organization to ensure that the OH&SMS meets the requirements of ISO 45001. This means that the organization must ensure that their OH&SMS is in compliance with the international standard and that all necessary processes and procedures are in place to meet those requirements.
5.3.5 Submit reports on the performance of the OH&SMS
Subclause 5.3.5 states that the organization must submit reports on the performance of the OH&SMS. This means that the organization must regularly report on the effectiveness of the OH&SMS and any areas that need improvement. These reports should be accessible to relevant parties within the organization and may be required to be submitted to external parties.
5.4 Consultation and participation of workers
Clause 5.4 of ISO 45001 outlines the requirements for consultation and participation of workers in the organization's OH&S management system.
5.4.1 Establish, implement and maintain a process for consultation and participation of workers
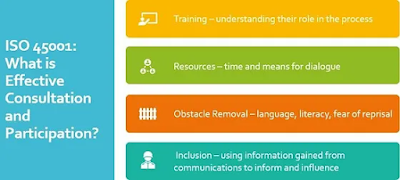
Subclause 5.4.1 requires the organization to establish, implement, and maintain a process for consultation and participation of workers. This process should ensure that workers have the opportunity to provide input and feedback on OH&S matters that affect them.
5.4.2 Provide mechanisms, time, training and resources
Subclause 5.4.2 requires the organization to provide the necessary mechanisms, time, training, and resources for workers to participate in the consultation process. This includes providing access to information and communication tools, as well as training on how to use them.
5.4.3 Provide timely access to relevant information
Subclause 5.4.3 requires the organization to provide workers with timely access to relevant information about OH&S matters. This includes information about hazards, risks, and controls, as well as any changes to the OH&S management system.
5.4.4 Determine and remove obstacles and barriers
Subclause 5.4.4 requires the organization to identify and remove any obstacles or barriers that prevent workers from participating in the consultation process. This includes addressing any cultural, language, or physical barriers that may exist.
5.4.5 Emphasize the consultation of non-managerial workers
Subclause 5.4.5 emphasizes the importance of consulting with non-managerial workers. This includes ensuring that non-managerial workers have the same opportunity to provide input and feedback as managerial workers.
ISO 45001 Clause 6: Planning
ISO 45001 clause 6 is divided into two sub clause- 6.1 and 6.2
Actions to address risks and opportunities
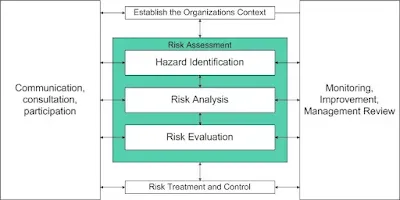
Actions to address risks and opportunities subclause outlines the steps that an organization must take to identify and assess potential hazards and risks, as well as opportunities for improvement. It includes the general requirements for risk management, the process for identifying and assessing hazards, the determination of legal and other requirements that must be met, and the planning of actions to address identified risks and opportunities.
6.1.1 General
This subclause provides an overview of the overall risk management process and the organization's commitment to addressing risks and opportunities.
6.1.2 Hazard identification and assessment of risks and opportunities
This subclause details the process for identifying and assessing hazards, including the methods and criteria used to evaluate potential risks and opportunities.
6.1.3 Determination of legal requirements and other requirements
Determination of legal requirements and other requirements subclause specifies the legal and other requirements that must be met by the organization, including regulatory, industry-specific, and customer requirements.
6.1.4 Planning action
This subclause outlines the steps that the organization must take to develop and implement plans to address identified risks and opportunities, including the resources required and the roles and responsibilities of individuals involved in the process.
6.2 OH&S objectives and planning to achieve them
This clause outlines the requirements for an organization to establish and maintain Occupational Health and Safety (OH&S) objectives and to plan for achieving those objectives
6.2.1 OH&S objectives
This subclause specifies the requirements for an organization to set OH&S objectives that align with the OH&S policy and the strategic direction of the organization. These objectives should be measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
6.2.2 Planning actions to achieve OH&S objectives
This subclause details the requirements for an organization to plan and implement actions necessary to achieve the established OH&S objectives. This includes identifying the resources needed, assigning responsibility for achieving the objectives, and implementing a system for monitoring and reviewing progress. The organization should also take into account any legal and other requirements when planning these actions.
ISO 45001 Clause 7: Support
It outlines the resources, competence, and awareness that an organization must have in order to effectively implement and maintain an Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) management system. ISO 45001 clause 7 is divided into five sub clause- 7.1,7.2,7.3,7.4 and 7.5
7.1 Resources
Resources refers to the materials, equipment, and personnel that an organization must have available in order to establish, implement, maintain, and improve an OHS management system. This includes resources for training, communication, and emergency response.
7.2 Competence
Competence refers to the knowledge, skills, and qualifications that employees must have in order to effectively perform their roles in the OHS management system. This includes training and education programs to ensure that employees are able to identify and mitigate hazards in the workplace.
7.3 Awareness
Awareness refers to the level of understanding and attention that employees and other relevant parties must have regarding the OHS management system and its importance in the organization. This includes communicating the importance of OHS to employees, providing information and training on hazards and risks, and encouraging participation in the OHS management system.
7.4 Communication
This clause outlines the requirements for communication within an organization regarding its OH&S management system. It covers both internal and external communication, and ensures that all relevant information is effectively and efficiently shared throughout the organization.
7.4.1 General
This subclause provides general guidance on communication within the organization, including the importance of clear and consistent messaging, and the need for effective communication channels to be established.
7.4.2 Internal communication
This subclause outlines the specific requirements for communication within the organization. It covers the need for clear roles and responsibilities to be established, and the importance of effective communication channels to be established to ensure that all relevant information is shared in a timely manner.
7.4.3 External communication
This subclause covers the requirements for communication with external stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, and regulatory bodies. It covers the need for clear and consistent messaging, and the importance of effective communication channels to be established to ensure that all relevant information is shared in a timely manner.
7.5 Documented information
Documented information refers to any written, recorded or electronic information that the organization uses to plan, establish, implement, maintain, and improve its OH&S management system. This includes documents such as policies, procedures, work instructions, and records.
7.5.1 General
General refers to the overall requirements for documented information within the organization's OH&S management system. This includes the need for the organization to determine the type and amount of documented information needed to support the effective planning, implementation, and operation of its OH&S management system, as well as the need to ensure that the information is accurate, up-to-date, and easily accessible.
7.5.2 Creating and updating
Creating and updating refers to the process of creating and updating documented information within the organization's OH&S management system. This includes the need for the organization to establish procedures for creating and updating documented information, as well as the need to ensure that the information is reviewed and approved by the appropriate personnel before it is released.
7.5.3 Control of documented information
Control of documented information refers to the process of ensuring that the organization's documented information is controlled and maintained in a consistent and effective manner. This includes the need for the organization to establish procedures for controlling and maintaining its documented information, as well as the need to ensure that the information is easily accessible and retrievable when needed.
ISO 45001 Clause 8: Operation
Clause 8 of ISO 45001 focuses on the operation of an organization's Occupational Health and Safety (OH&S) management system. It outlines the requirements for planning and controlling the operation of the system to ensure the safety and health of employees and others who may be affected by the organization's activities. ISO 45001 clause 8 is divided into two sub clause- 8.1 and 8.2
8.1 Operational planning and control
Subclause 8.1, Operational planning and control, covers the general requirements for planning and controlling the operation of the OH&S management system.
It includes specific subclauses for:
8.1.1 General: This subclause outlines the overall requirements for operational planning and control, including the need for the organization to identify and assess hazards and risks, and implement appropriate controls to eliminate or reduce these hazards and risks.
8.1.2 Eliminating Hazards and reducing OH&S risks: This subclause addresses the need for the organization to identify and assess hazards and risks, and implement appropriate controls to eliminate or reduce these hazards and risks.8.1.3 Management of change: This subclause outlines the requirements for managing changes to the OH&S management system, including assessing the potential impact of the change on the safety and health of employees and others who may be affected by the organization's activities.
8.1.4 Procurement: This subclause addresses the need for the organization to consider the OH&S risks associated with the procurement of goods and services, and to include OH&S requirements in contracts and agreements with suppliers and contractors.
Subclause 8.2, Emergency preparedness and response, covers the requirements for the organization to have emergency preparedness and response procedures in place, including the need for regular training and drills for employees and others who may be affected by the organization's activities. This subclause also addresses the need for the organization to have plans in place to respond to emergency situations, including evacuation procedures and emergency communication plans.
ISO 45001 Clause 9: Performance evaluation
This clause outlines the requirements for monitoring, measuring, analyzing, and evaluating the effectiveness of the system.
ISO 45001 clause 9 is divided into three sub clause- 9.1,9.2, and 9.3
9.1 Monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation
This subclause lays out the requirements for monitoring and measuring the OHS performance of the organization and analyzing the data collected to evaluate the effectiveness of the system.
9.1.1 General
This sub-subclause provides an overview of the requirements for monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation outlined in 9.1.
9.1.2 Evaluation of compliance
This sub-subclause specifies the requirements for evaluating compliance with relevant legal and other requirements related to OHS.
9.2 Internal audit
g
9.2.1 General
This sub-subclause provides an overview of the requirements for internal audits outlined in 9.2.
9.2.2 Internal audit program
This sub-subclause specifies the requirements for developing and implementing an internal audit program.
9.3 Management review
9.3.1 General
This sub-subclause provides an overview of the requirements for management reviews outlined in 9.3.
9.3.2 Review inputs
This sub-subclause specifies the information and data that should be considered during a management review.
9.3.3 Review outputs
This sub-subclause outlines the results and decisions that should come out of a management review.
ISO 45001 Clause 10: Improvement
ISO 45001 clause 10 is divided into three sub clause- 10.1,10.2, and 10.3
10.1 General
This sub clause outlines the general requirements for an organization to improve its OH&S management system. It specifies that the organization must establish, implement, maintain and continually improve its OH&S management system in order to achieve its OH&S objectives and improve overall performance.
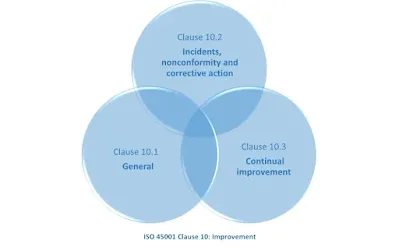
10.2 Incident, nonconformity and corrective actions
This sub clause outlines the requirements for an organization to identify, investigate and take corrective action for any incidents, nonconformities or other issues that arise in the OH&S management system. This includes identifying the root cause of the problem, taking appropriate corrective action, and implementing measures to prevent recurrence.
10.3 Continual improvement
This sub clause outlines the requirements for an organization to continuously improve its OH&S management system. This includes setting objectives and targets, monitoring performance, and making necessary changes to improve overall performance. The organization must also review the effectiveness of its OH&S management system and make any necessary changes to ensure it remains effective.
Annex A (informative) Relationship between ISO 45001:2018 and OHSAS 18001:2007
Annex A (informative) of ISO 45001:2018 provides information on the relationship between the new ISO 45001:2018 standard and the previous OHSAS 18001:2007 standard for Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems. This annex explains the similarities and differences between the two standards and how organizations can transition from OHSAS 18001:2007 to ISO 45001:2018. It highlights the key changes in the new standard, such as a greater emphasis on leadership and worker participation, as well as a more robust risk management process. It also provides guidance on how to align existing OHSAS 18001:2007 systems with the requirements of ISO 45001:2018. Overall, Annex A provides useful information for organizations that are looking to upgrade their existing OH&S management systems to the new ISO 45001:2018 standard.
Annex B (informative) Correspondence between ISO 45001:2018 and ISO 9001:2015
Annex B (informative) of ISO 45001:2018 provides information on the correspondence between ISO 45001:2018 and ISO 9001:2015, which is the standard for Quality Management Systems. This annex explains how the requirements of ISO 45001:2018 align with those of ISO 9001:2015 and how organizations can integrate the two standards for a more efficient and effective management system.
Annex B highlights the similarities between the two standards in terms of structure, terminology, and common requirements such as risk management, leadership, and continuous improvement. It also explains how the specific requirements of ISO 45001:2018 for Occupational Health and Safety can be integrated with the general requirements of ISO 9001:2015 for Quality Management.
This annex is particularly useful for organizations that already have an ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management System in place and are looking to integrate OH&S management within it. It also helps organizations to understand how to implement both standards in a harmonized way in order to avoid duplication and increase efficiency. Overall, Annex B provides guidance on how to integrate ISO 45001:2018 and ISO 9001:2015 effectively to achieve a more comprehensive management system.
Annex C (informative) Correspondence between ISO 45001:2018 and ISO 14001:2015.
Annex C (informative) of ISO 45001:2018 provides information on the correspondence between ISO 45001:2018 and ISO 14001:2015, which is the standard for Environmental Management Systems. This annex explains how the requirements of ISO 45001:2018 align with those of ISO 14001:2015 and how organizations can integrate the two standards for a more efficient and effective management system.
Annex C highlights the similarities between the two standards in terms of structure, terminology, and common requirements such as risk management, leadership, and continuous improvement. It also explains how the specific requirements of ISO 45001:2018 for Occupational Health and Safety can be integrated with the general requirements of ISO 14001:2015 for Environmental Management.
This annex is particularly useful for organizations that already have an ISO 14001:2015 Environmental Management System in place and are looking to integrate OH&S management within it. It also helps organizations to understand how to implement both standards in a harmonized way in order to avoid duplication and increase efficiency. Overall, Annex C provides guidance on how to integrate ISO 45001:2018 and ISO 14001:2015 effectively to achieve a more comprehensive management system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What
is occupational health? Occupational health refers to the branch of
medicine and hygiene that deals with the identification and prevention of
health hazards in the workplace. It focuses on ensuring the physical,
mental, and social well-being of employees while they are at work.
- What
is occupational health and safety? Occupational health and safety
(OHS) is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the protection of
workers' health and safety in their workplace. It involves identifying
potential hazards, assessing risks, and implementing measures to ensure a
safe and healthy work environment.
- Why
is occupational health and safety important? Occupational health and
safety are essential for several reasons. It protects employees from
workplace injuries and illnesses, reduces absenteeism, improves
productivity, enhances employee morale, and ensures legal compliance,
ultimately leading to a more sustainable and efficient organization.
- Are
road accidents part of occupational safety and health? Yes, road
accidents can be considered a part of occupational safety and health,
especially when they occur during work-related travel or as a part of an
employee's job responsibilities. Employers should address road safety as
part of their overall occupational health and safety program.
- What
happens during an occupational health assessment? An occupational
health assessment involves evaluating an employee's health and fitness to
perform specific job tasks. It may include medical examinations, health
history reviews, and assessments of physical and mental capabilities
relevant to the job.
- What
is an occupational health check? An occupational health check is a
medical examination conducted to assess an employee's health in the
context of their job requirements. It helps identify any health issues
that may affect their ability to work safely and effectively.
- What
is an occupational health assessment? An occupational health
assessment is a comprehensive evaluation of an individual's health and
work environment to determine potential risks and hazards associated with
their job. The assessment aims to recommend preventive measures to protect
the worker's well-being.
- How
to create awareness for worker's safety and health? Creating awareness
for worker's safety and health involves providing regular training,
conducting safety seminars, displaying safety signage, and encouraging
open communication about safety concerns. Employees should be educated
about risks and safe practices in the workplace.
- Why
is workplace safety important? Workplace safety is crucial as it
prevents accidents, injuries, and illnesses among employees. It enhances
employee satisfaction and productivity, reduces business costs, and
promotes a positive work culture.
- How
to improve health and safety in the workplace? To improve health and
safety in the workplace, organizations should conduct risk assessments,
implement safety policies and procedures, provide proper training,
encourage employee involvement in safety programs, and regularly review
and update safety measures.
- What
is personal safety in the workplace? Personal safety in the workplace
refers to individual responsibility for maintaining one's safety by
following safety guidelines, wearing personal protective equipment (PPE),
and being aware of potential hazards in the work environment.
- Why
should we manage workplace health and safety? Managing workplace
health and safety is essential to protect employees from harm, comply with
legal requirements, improve overall productivity, enhance employee morale,
and demonstrate a commitment to the well-being of the workforce.
- How
to ensure safety in the workplace for nurses? Ensuring safety in the
workplace for nurses involves providing appropriate training on handling
medical equipment and hazardous materials, maintaining a clean and
organized workspace, implementing infection control measures, and
promoting a supportive work environment.
- How
to maintain health and safety practices in the workplace? To maintain
health and safety practices in the workplace, organizations should
establish clear safety protocols, conduct regular safety inspections,
encourage reporting of safety concerns, and foster a safety-oriented
culture among employees.
- What
event had an enormous effect on US workplace safety? The passage of
the Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) in 1970 had an enormous
effect on US workplace safety. OSHA established guidelines and standards
to ensure safe and healthy working conditions for employees across various
industries.
- What
is safety awareness in the workplace? Safety awareness in the
workplace refers to the consciousness and understanding of potential
hazards and risks, as well as the proactive adoption of safe practices by
all employees to prevent accidents and injuries.
It is important to work with a reputable ISO consultant like ISO Certification in Nepal Pvt. Ltd. that can provide cost effective expert guidance and support to your organization throughout the process of ISO 9001 implementation. We are the leading ISO System Certification body in Nepal. We will help an organization to understand requirements, implement the standard and ensure that your company is in compliance with any ISO Certification in Nepal. Besides to ISO 9001 quality management system, we also provide ISO 14001( Environmental management System certification) , ISO 22000(Food Safety Management System Certification) ISO 45001 Occupational health and safety management system , ISO 27001 Information Security Management System . ISO/IEC 17025 Testing and calibration laboratories Organic Certification in Nepal. If you have any queries as well as if you want to get your organization to be ISO Certified, please call 9840525565 to get free consultation on ISO Certification service and know which ISO standards is best for your organization.






.png)